created, $=dv.current().file.ctime & modified, =this.modified
tags:mereology
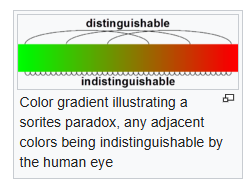
With the assumption that removing a single grain does not cause a heap to not be considered a heap anymore, the paradox is to consider what happens when the process is repeated enough times that only one grain remains and if it is still a heap.
Resolution
- Heaps do not exist
- Setting a fixed boundary
- boundary remains arbitrary, with little significance of 999 to 1K grains
- Fixed boundaries, not necessarily knowable
- Supervaluationism
- a proposition can have a definite truth value, even when its components do not.
- “Pegasus likes licorice” has no truth-value given Pegasus doesn’t refer but “Pegasus likes licorice or Pegasus doesn’t like licorice” is a valid schema so according to supervaluationism it would be true regardless, or supertrue or superfalse
- Fuzzy logic
- a continual spectrum of logical states where sand transition gradually from definitely heap to definitely not heap.
- Hysteresis
- using knowledge of what the collection of sand started as