created 2025-02-25, & modified, =this.modified
Abstract: Recent large language models (LLMs) can generate and revise text with human-level performance, and have been widely commercialized in systems like ChatGPT. These models come with clear limitations: they can produce inaccurate information, reinforce existing biases, and be easily misused. Yet, many scientists have been using them to assist their scholarly writing. How wide-spread is LLM usage in the academic literature currently? To answer this question, we use an unbiased, large-scale approach, free from any assumptions on academic LLM usage. We study vocabulary changes in 14 million PubMed abstracts from 2010–2024, and show how the appearance of LLMs led to an abrupt increase in the frequency of certain style words. Our analysis based on excess words usage suggests that at least 10% of 2024 abstracts were processed with LLMs. This lower bound differed across disciplines, countries, and journals, and was as high as 30% for some PubMed sub-corpora. We show that the appearance of LLM-based writing assistants has had an unprecedented impact in the scientific literature, surpassing the effect of major world events such as the Covid pandemic.
Excess word usage suggests at least 10% of papers were processed with LLMs, with as high as 30% for some sub-corpora.
Major events affect word frequency. The rise and fall of scientific disciplines is traceable in scholarly writing.
Attempts to quantify use in scientific papers falls into three groups
- LLM detectors, which are blackbox models trained based on Ground Truth human and LLM text.
- modeled word frequency distribution in scientific corpora as a mixture distribution of texts produced by humans and by LLMs
- lists of marker words, known to be used by LLMs which are stylistic words unrelated to text contents

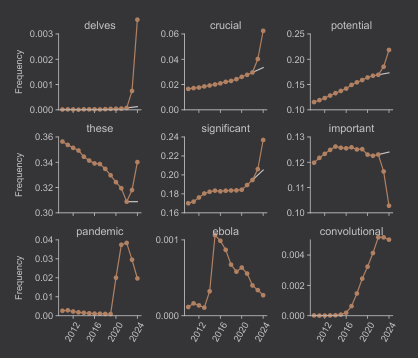
- By meticulously delving into the intricate web connecting … and … this comprehensive chapter takes a deep dive into their involvement as significant risk factors for
- A comprehensive grasp of the intricate interplay between … and … is pivotal for effective therapeutic strategies.
- Initially, we delve into the intricacies of …, accentuating its indispensability in cellular physiology, the enzymatic labyrinth governing its flux, and the pivotal … mechanisms.
We argue that the true LLM usage in academic writing may be closer to the highest lower bounds we observed, as those may be corpora where LLM usage is the least disguised and the easiest to detect. These estimates are around 30%, which is in line with recent surveys on researchers’ use of LLMs for manuscript writing.
LLM usage We did not use ChatGPT or any other LLMs for writing the manuscript or for performing the data analysis.